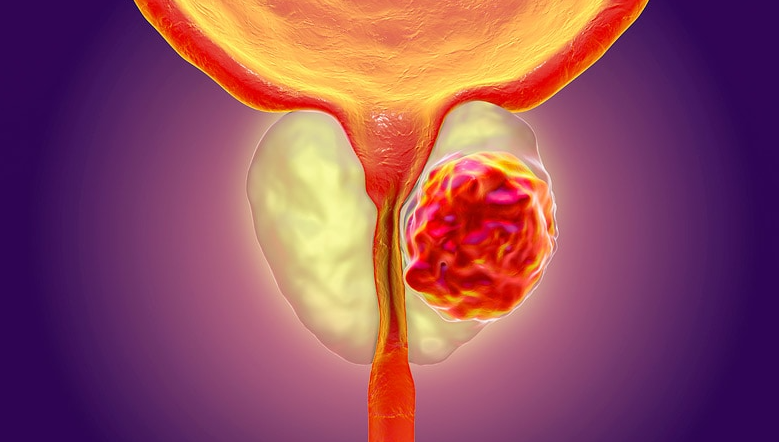
A groundbreaking research effort involving teams from the University of Virginia, Mount Sinai, the University of Michigan, the University of Texas, and others has displayed the clinical efficacy of an innovative therapy that utilizes nanoparticles and laser guidance for prostate cancer treatment. The findings were published in the Journal of Urology.
The research, involving 44 men with localized prostate cancer, utilized gold nanoshells in conjunction with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound fusion—an advanced technique that improves MRI data—to accurately target and destroy cancerous prostate tissue.
Gold nanoshells are microscopic particles, thousands of times smaller than a human hair, engineered to absorb specific wavelengths of light and produce heat effectively. In this study, the gold nanoshells were tailored to concentrate on tumours, enabling precise near-infrared laser treatment that heats and eradicates cancerous tissue while preserving the surrounding healthy cells.
This cutting-edge approach, known as nanoparticle-directed focal photothermal ablation, successfully eradicated cancerous cells in 73 % of patients after 12 months, as confirmed by negative biopsies in the treated regions. The treatment achieved these outcomes while preserving essential functions, including urinary and sexual health, and without any observed side effects, substantially enhancing patients' quality of life.
Our findings represent a major step forward in prostate cancer treatment. This therapy not only effectively eliminates cancerous cells but also preserves key quality-of-life factors, which is a huge win for patients. Jennifer L. West, Ph.D., Dean, School of Engineering and Applied Science, University of Virginia. West concludes, “This study showcases the strength of interdisciplinary collaboration. Together, we’re pushing the boundaries of what's possible in cancer treatment, and it's exciting to be at the forefront of this innovation.”
Source: AZoNano
This cutting-edge approach, known as nanoparticle-directed focal photothermal ablation, successfully eradicated cancerous cells in 73 % of patients after 12 months